In today’s digital world, where cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, ensuring the security of business assets in the cloud is paramount. Google Cloud Platform (GCP), a leading cloud computing platform, offers a converged security portfolio designed to protect your valuable data and applications from evolving threats. This article explores the key benefits of GCP’s security approach and showcases real-world examples of its effectiveness.

Key Benefits of Google Cloud’s Converged Security Portfolio
- A Comprehensive, Multi-Layered Security Approach:
Google Cloud’s converged security portfolio takes a multi-layered approach, addressing various aspects of cloud security to provide a robust defense. This comprehensive strategy includes:
- Infrastructure Security: Google is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, encompassing hardware, hypervisors, and the physical network, offering a secure foundation for customer workloads.
- Network Security: Google Cloud enables users to establish isolated network environments using Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). VPCs, coupled with customizable firewall rules, provide control over network traffic, effectively blocking unauthorized access and safeguarding applications and data.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive information is paramount, and Google Cloud employs robust encryption methods for data both at rest and in transit. This ensures data confidentiality and integrity throughout its lifecycle.
- Application Security: Google offers tools and services designed to secure applications deployed on its platform. While Google manages the underlying infrastructure for services like container orchestration, VMs, and firewalls, users are responsible for their application data and the software itself.
- Software Supply Chain Security: Google Cloud manages marketplace images and templates, guaranteeing their integrity. However, users are responsible for patching the OS and software once deployed, maintaining security scans, and managing the software bill of materials used by their applications.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controlling access is crucial for cloud security. Google Cloud’s IAM allows users to manage identities and authorize actions on specific services or resources, providing granular control over who can access and modify sensitive data and resources.
- Security Monitoring and Operations: Google Cloud provides a comprehensive suite of security services, including Cloud Monitoring, Cloud Logging, and Security Command Center. These tools facilitate real-time visibility, threat detection, and effective security management.
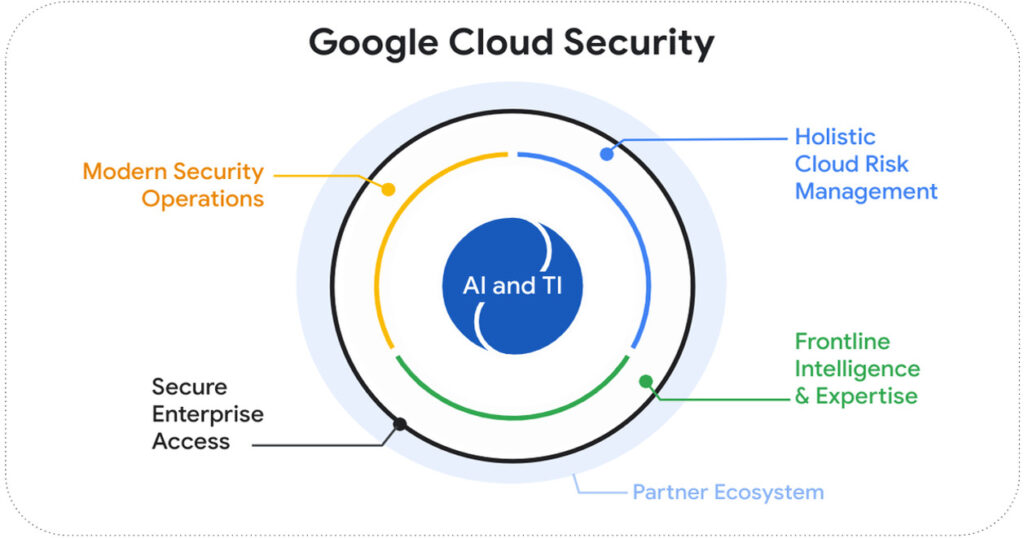
- The Power of AI in Security Operations:
AI and machine learning are key components of Google Cloud’s security strategy. They automate tasks, deliver intelligent insights, and facilitate faster response times, significantly strengthening security operations. Examples of AI in action include:
- Mandiant Custom Threat Hunt: This service, an addition to Google Cloud’s threat hunting offering, uses AI to uncover current or past threat actor activity, complementing existing detection and response services.
- Security Command Center (SCC) Virtual Red Teaming: SCC utilizes AI-driven virtual red teaming to proactively simulate attack paths and identify “toxic combinations” of security issues that could lead to significant vulnerabilities. By proactively identifying these risks, organizations can remediate them before they’re exploited.
- Gemini in Security Operations: Google’s Gemini AI platform is changing how security teams operate. Its assisted investigation features guide security analysts through complex investigations by contextualizing data from Google Threat Intelligence and MITRE, leading to quicker threat detection and response.
- The Shared Fate Model:
Google Cloud embraces a shared fate model, recognizing the interdependence of its security and that of its customers. This collaborative approach involves:
- Enterprise Foundations Blueprint: Google Cloud offers blueprints that cover top security concerns and best practices, guiding users on how to secure their cloud environments effectively.
- Secure Blueprints with Infrastructure-as-Code: Google provides secure blueprints leveraging Infrastructure-as-Code to automate the deployment of secure environments. This automation minimizes the risk of misconfigurations and strengthens the overall security posture.
- Architecture Framework with Built-in Security Best Practices: Google’s architecture framework incorporates security best practices, ensuring a secure-by-default approach to cloud deployments. This proactive stance helps organizations build security into the foundation of their cloud environments.
- Maintaining Compliance with Continuous Monitoring:
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is a priority for Google Cloud, and it provides a range of tools and features to assist organizations in meeting their compliance obligations. Key areas include:
- Assured Workloads: This service helps organizations accelerate their compliance journey by offering automated controls and guardrails for sensitive workloads, particularly those subject to regulations like HIPAA and FedRAMP.
- Compliance Monitoring and Automation: Google Cloud provides tools for continuous compliance monitoring and the automation of security tasks, ensuring consistent adherence to policies and regulations. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of compliance violations and strengthens the overall security posture.
- The Power of Partner Integrations:
Recognizing that security is a collaborative effort, Google Cloud promotes the integration of its security solutions with existing security ecosystems. It seamlessly integrates with various third-party tools and has cultivated strategic partnerships to bolster its security offerings. Examples include:
- Mandiant Threat Intelligence: Google Cloud integrates Mandiant’s expertise in threat intelligence and incident response, giving customers access to valuable insights and proactive threat detection capabilities.
- Integration with SIEM Systems: Google Cloud’s logging tools can be integrated with enterprise-wide SIEM systems. This integration provides centralized security monitoring and streamlines incident response, simplifying security management for organizations.
- NordLayer Integration: NordLayer provides external security solutions that complement Google Cloud’s internal features, enhancing access control, network segmentation, and data encryption, and contributing to robust GCP deployments.
Conclusion
Google Cloud’s converged security portfolio offers a comprehensive and effective approach to securing cloud environments in the face of evolving cyber threats. By combining multiple layers of security, leveraging AI and threat intelligence, embracing a shared fate model, ensuring continuous compliance monitoring, and collaborating with partners, Google Cloud empowers businesses to confidently adopt cloud computing while mitigating cybersecurity risks in the digital landscape. Through continuous innovation and a commitment to security, Google Cloud continues to provide a robust and reliable platform for organizations seeking to thrive in the cloud.
Sources:
https://cloud.google.com/security
https://cloud.google.com/security/solutions/security-and-resilience